-
Home > News
Classification and Applications of Insulators
Classification of Insulators
Insulators can be classified into high-voltage insulators and low-voltage insulators based on their operating voltage.
Insulators can be classified into porcelain insulators, glass Insulators, and organic material (epoxy resin cast) insulators based on their manufacturing materials.
 |  |  |
| glass insulators | porcelain insulators | composite insulator |
Insulators can be categorized into indoor and outdoor types based on their installation locations.
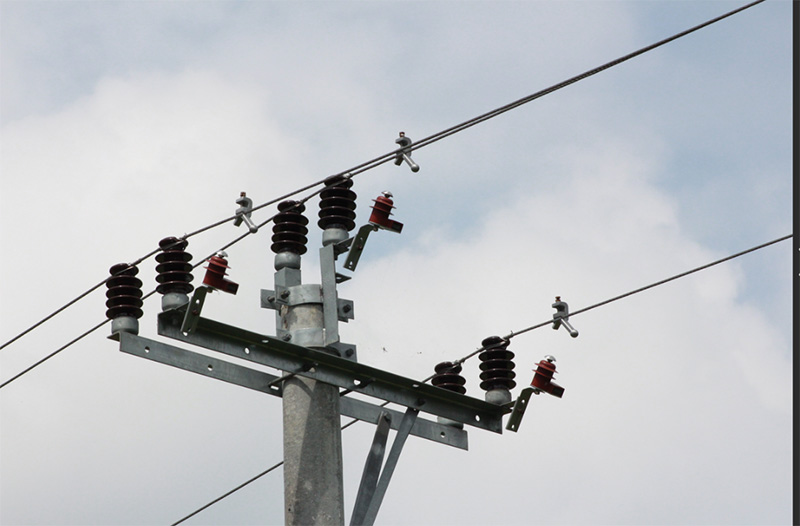
Insulators can be classified into 11 subcategories and 48 series based on their structure and application.
1) High-Voltage Line Insulators
① High-Voltage Line Rigid Insulators: Include pin-type porcelain insulators, porcelain cross-arm insulators, and shackle-type porcelain insulators.
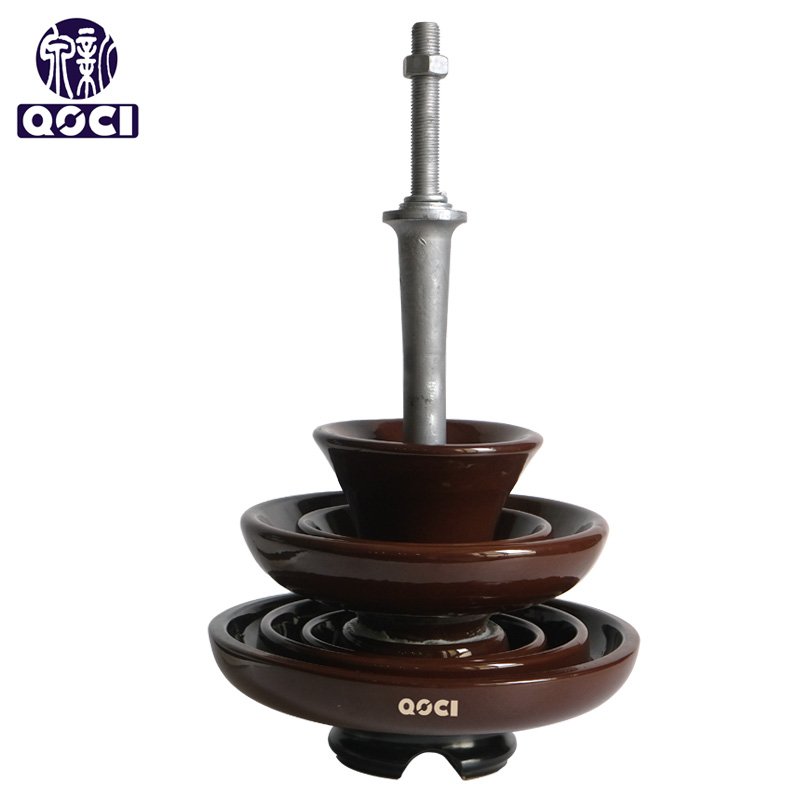 |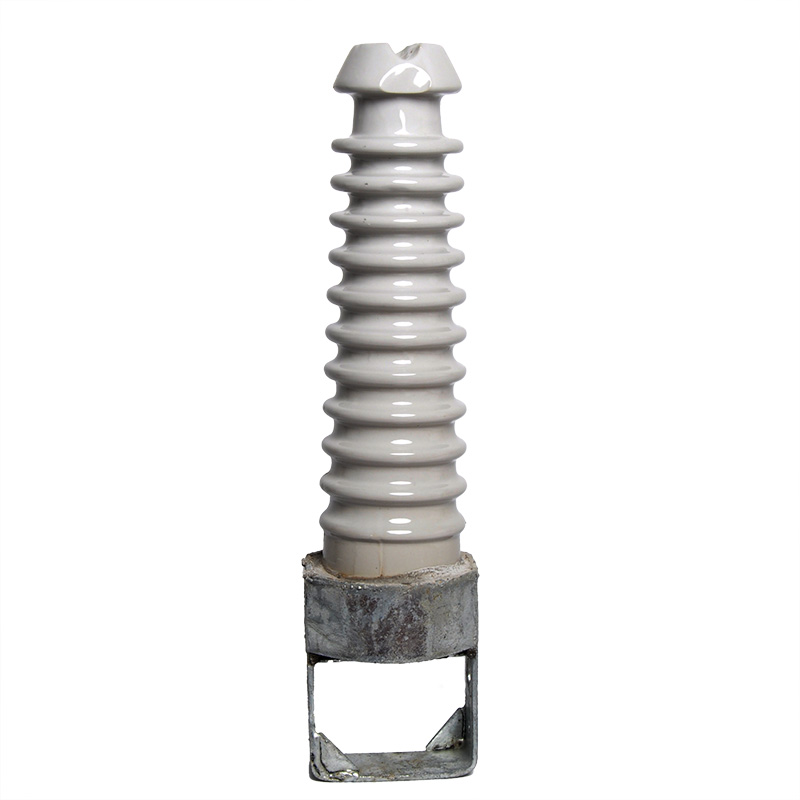  |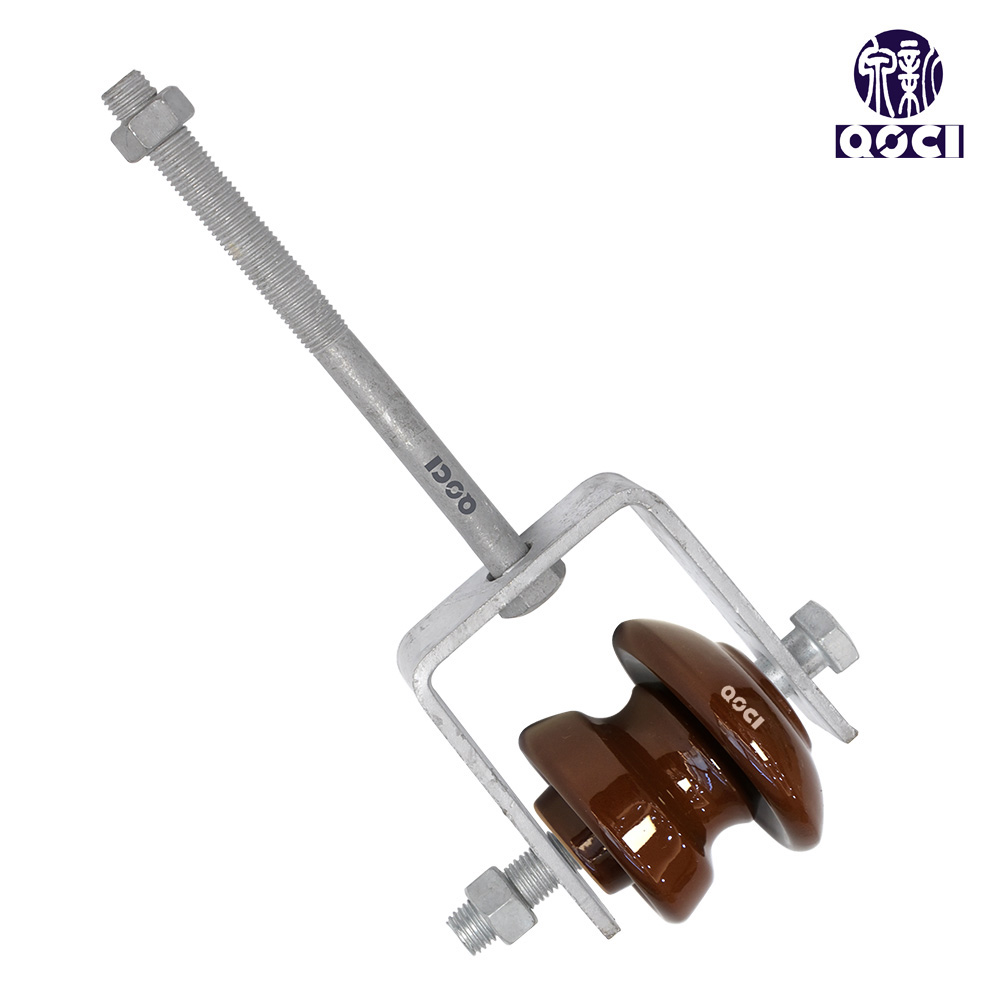  |
| pin-type porcelain insulators | porcelain cross-arm insulators | shackle-type porcelain insulators |
* High-Voltage Line Porcelain Cross-Arm Insulators: Classified by structure into all-porcelain type, cement-fitted type, single-arm type, and V-type; by installation method into vertical and horizontal types; and by 50% full-wave impulse flashover voltage into levels such as 185kV, 210kV, 280kV, 380kV, 450kV, 610kV. Used in high-voltage overhead transmission and distribution lines, they can replace pin-type and suspension insulators and eliminate the need for tall pole cross-arms.
* High-Voltage Line Shackle-Type Porcelain Insulators: Rated for 6kV and 10kV levels. Used at terminals, strain, and corner poles of overhead transmission/distribution lines for insulating and securing conductors. Also widely used in conjunction with line suspension insulators as a component in line hardware, simplifying hardware structure.
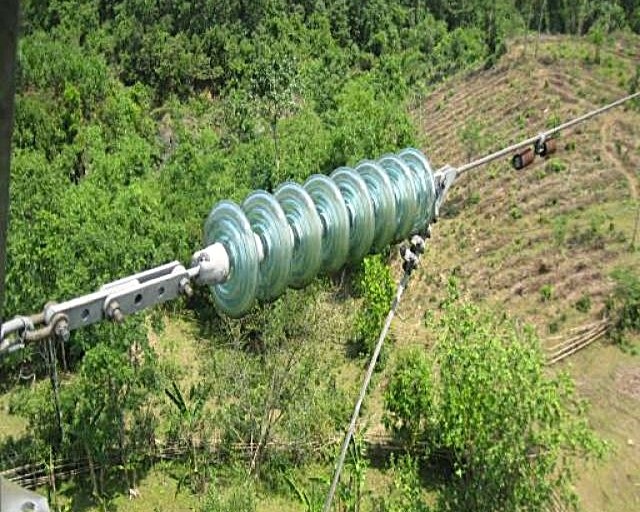
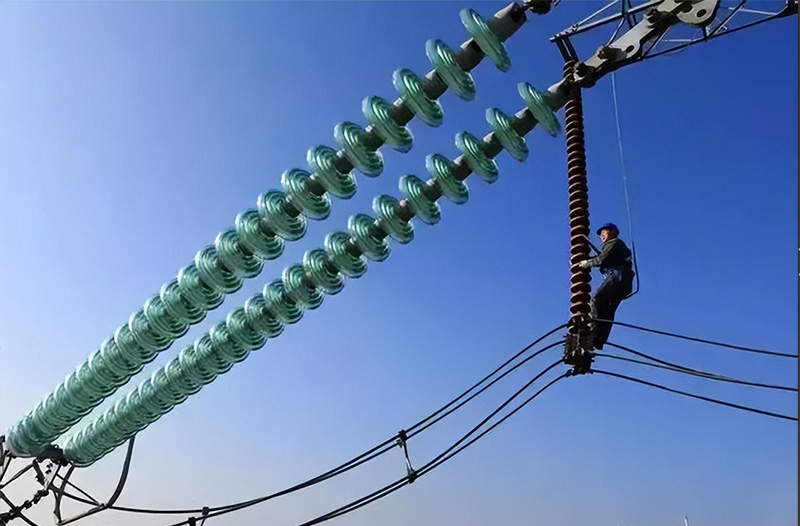
② High-Voltage Line Suspension Insulators: Include cap-and-pin porcelain insulators, cap-and-pin glass insulators, Long-rod porcelain insulators, and Ground - wires insulators.
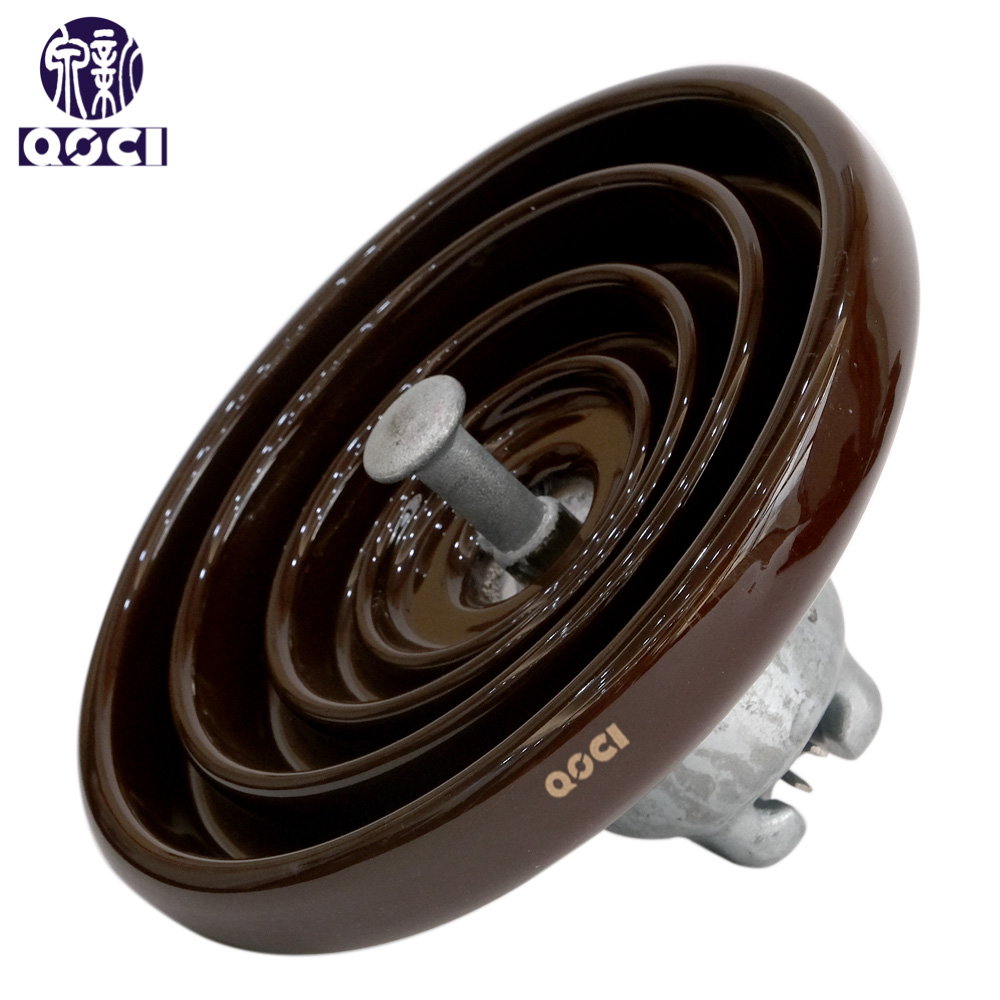 |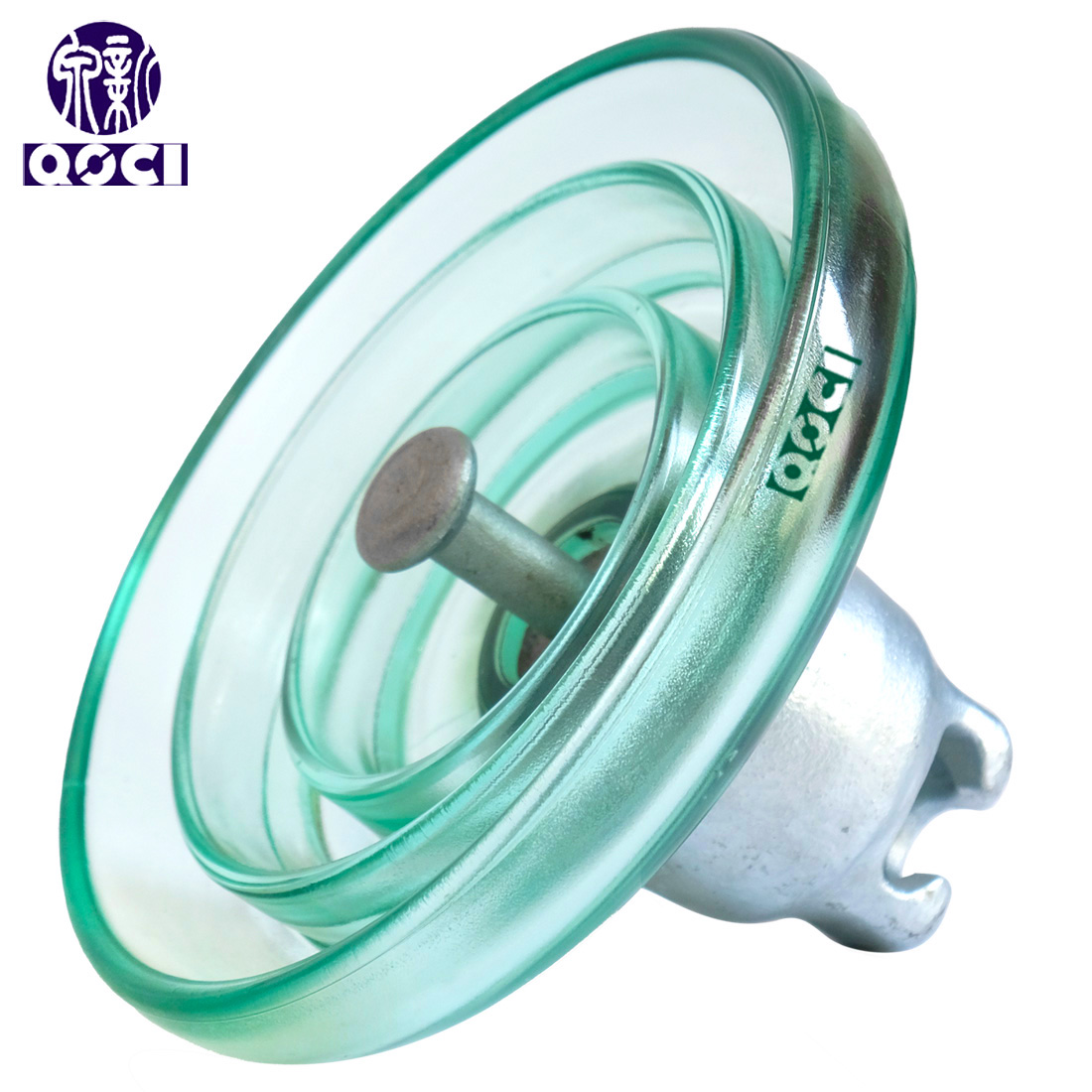  |  |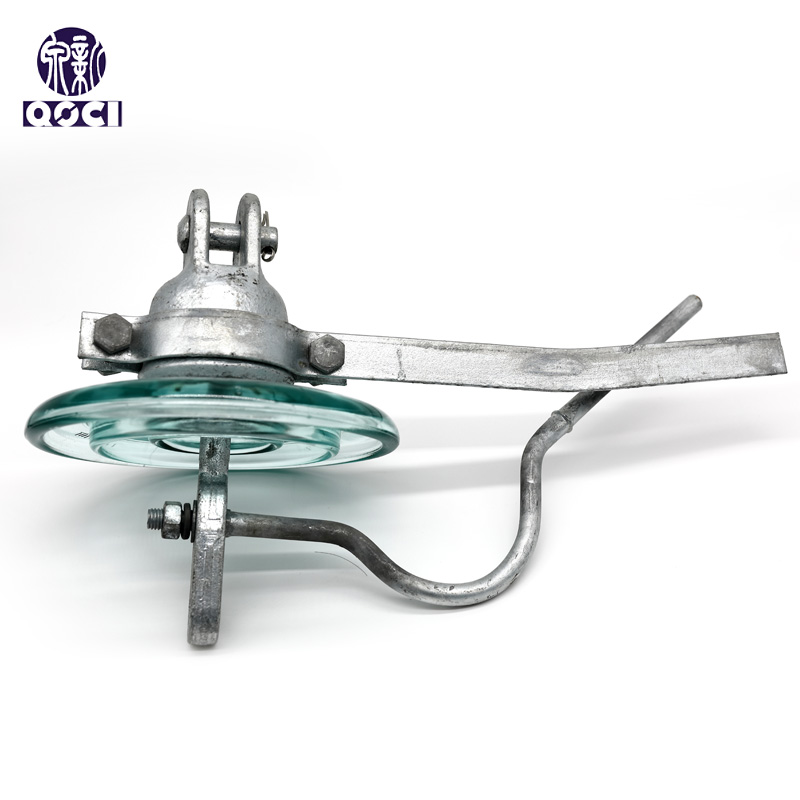  |
| Cap&pin porcelain insulators | Cap&pin glass insulators | Long-rod porcelain insulators | Ground - wires insulators |
* High-Voltage Line Cap-and-Pin Porcelain Insulators: Divided into standard type and anti-pollution type. Used in high-voltage and extra-high-voltage transmission lines to suspend or tension conductors and insulate them from towers/poles. Suspension insulators feature high mechanical and electrical strength, can be adapted to various voltage levels and strength requirements through different string configurations, making them the most widely used type. The standard type is suitable for general industrial areas. Compared to standard type, the anti-pollution type has greater creepage distance and a shape facilitating cleaning by rain/wind, suitable for coastal areas, metallurgical/chemical powder pollution, and areas with severe industrial contamination. Using anti-pollution insulators in such areas allows for smaller tower/pole dimensions, offering significant economic value.
* High-Voltage Line Cap-and-Pin Glass Insulators: Their application is essentially the same as cap-and-pin porcelain insulators. Glass insulators offer advantages such as high mechanical strength, resistance to mechanical shock, good thermal shock performance, long service life, excellent electrical performance and lightning withstand capability. Furthermore, upon failure in service, the shed disc breaks automatically, making detection easy and significantly reducing insulation inspection workload.
* High-Voltage Long-rod porcelain insulators: Used on terminal, strain, and corner poles of overhead power lines rated 10kV and below for insulating and securing conductors. They can replace some shackle-type porcelain insulators and cap-and-pin porcelain insulators.
③ Porcelain Long-Rod Insulators for Railway Catenary
2) Low-Voltage Line Insulators
① Low-Voltage Line Pin-Type, Shackle-Type, and Spool-Type Porcelain Insulators:
* Low-Voltage Line Pin-Type Porcelain Insulators: Used in overhead power lines below 1kV for insulating and securing conductors.
* Low-Voltage Line Shackle-Type Porcelain Insulators: Used on terminal, strain, and corner poles of distribution lines for insulating and securing conductors.
* Low-Voltage Line Spool-Type Porcelain Insulators: Used on terminal, strain, and corner poles of distribution lines for insulating and securing conductors.
② Overhead Line Strain Porcelain Insulators: Used on AC/DC overhead transmission/distribution lines and communication line terminal corners or poles with long spans to balance the tension on poles, serving as strain insulation and connection.
③ Trolley Line Insulators: Used as insulation and for tensioning conductors on trolley lines, or for insulating and supporting conductive parts on trolleys and at substations.
④ Communication Line Pin-Type Porcelain Insulators: Used in overhead communication lines for insulating and securing conductors.
⑤ Wiring Insulators: Include knob insulators, porcelain cleats, and porcelain tubes. Used for low-voltage wiring.
3) High-Voltage Substation Insulators
① High-Voltage Indoor Post Insulators for Substations: Used for busbars and equipment in indoor power stations and substations with power-frequency rated voltages of 6–35kV. They serve as insulating supports for high-voltage conductive parts. They are generally designed for installation at altitudes not exceeding 1000m, ambient temperatures of –40 to 40°C, and should be used under conditions free from pollution and condensation. Specially designed high-altitude types can be used in areas up to 3000m and 5000m.
② Outdoor Pin-Type Post Insulators: Suitable for the insulating parts or switchgear of electrical apparatus with AC rated voltages of 3–220kV, installed where ambient temperature is –40 to +40°C and altitude does not exceed 1000m, for insulating and securing conductors.
③ Outdoor Solid-Core Post Insulators: Used in high-voltage electrical apparatus and switchgear for insulating and securing conductors. They have largely replaced outdoor pin-type post insulators in usage.
④ Anti-Pollution Outdoor Solid-Core Post Insulators: Suitable for medium pollution areas with an equivalent salt deposit density (ESDD) up to 0.1 mg/cm², for insulating and securing functions in high-voltage electrical apparatus and switchgear.
⑤ High-Voltage Wall Bushings: Include indoor wall bushings, outdoor wall bushings, bushing wall bushings, and oil-impregnated paper capacitor wall bushings.
⑥ Porcelain Housings for Electrical Apparatus: Include transformer bushings/housings, switchgear bushings/housings, and instrument transformer bushings/housings.
* Transformer Bushings/Housings: Include two main categories: bushing housings and post housings for power transformers and testing transformers.
* Switchgear Bushings/Housings: Include housings for bulk oil circuit breakers, minimum oil circuit breakers, load break switches, explosion-proof switches, disconnectors (isolators), air circuit breakers, etc. Mainly used as insulation for the high-voltage leads of switches to ground and as containers for the insulation and internal insulation of circuit breakers.
* Instrument Transformer Bushings/Housings: Used as insulating components for current transformers and voltage transformers.